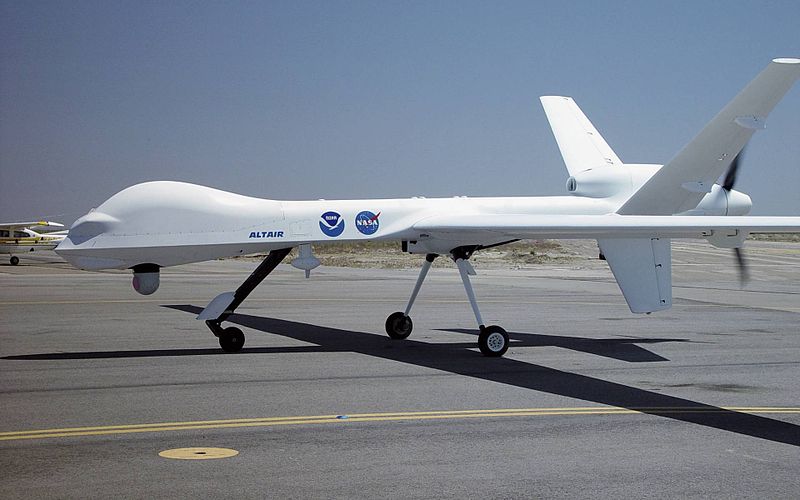
Until recently, the word “drone” evoked a buzzing sound or a stingless male bee. Today, however, its everyday use no longer derives from noises or the animal kingdom. The word “drone” is now better known as a synonym for “unmanned aircraft”. Yet, this is not a twenty-first-century invention. Some years ago they were called “remote control aircraft”, but progress has brought with it three new elements that have made it necessary to coin a new word: autonomous flight, distance from the remote pilot, and military use.
Until recently, the word “drone” evoked a buzzing sound or a stingless male bee. Today, however, its everyday use no longer derives from noises or the animal kingdom. The word “drone” is now better known as a synonym for “unmanned aircraft”. Yet, this is not a twenty-first-century invention. Some years ago they were called “remote control aircraft”, but progress has brought with it three new elements that have made it necessary to coin a new word: autonomous flight, distance from the remote pilot, and military use.
Although the drone’s lethal capacity has made it famous in the past decade, it also has civilian and commercial uses. The two giant companies Amazon and Google are presently competing over which will be able to use it as an urban delivery device, moving packages from warehouse to home in a couple of minutes. Many other companies have dreamt up further drone uses: cultivating fields, rescue work, checking rooftop plumbing, and getting better images for real-estate sales. Its commercial uses will dramatically expand after 2018 when new legislation comes into force in the United States. Drones are not only remotely piloted aircraft. Their new functions will include – if all goes well – a self-piloting version which can respond to software commands.
However, the lamentable fame of drones and the theme of the debate Drones. Siege at a distance is their impressive ability to kill. For the moment, only three countries have killed with drones: the United States, the United Kingdom and Israel. The military use of drones is not limited to firing missiles. Surveillance and reconnoitring are more common among their strategic uses. Most of the countries with drones – more than fifty – have this less offensive type. The future violence of drones will not only take the form of missile strikes. China (and no doubt other countries as well) is working on planes that can engage in electronic warfare: blocking GPS systems, or scrambling object-locating programmes.
Nevertheless, the lethal drones have been the most evident type and, moreover, they have been used as freely moving aerial spies, unthreatened by anti-aircraft defences and combat aircraft, in Pakistan, Afghanistan, Yemen and Gaza. Drones have been one of the two outstanding tools of President Obama’s antiterrorist campaign since 2008, the other being the special forces. Their effectiveness in a real war in which the enemy has anti-aircraft weapons is yet to be seen. Perhaps smaller, undetectable drones will be deployed. Some of them measure only 15 centimetres. Soon there will be autonomous solar-powered drones that can remain in the air for up to three years. A whole world to be discovered.
The constant activity of US drones in the remote zones of the world means that alleged members of Al-Qaeda and its affiliates will cannot live or train in peace. Obama has cut back their use in the past two years but the toll of civilian victims is still enormous. The rage of affected populations which are living under constant threat casts doubt on the success of this method.
Drones can be guided by human intelligence. Somebody informs that a target is, or will be at a certain place which is then attacked. But the target might be at a family gathering or party. What then? It will depend on the importance of the target for the attacking force. Drones have also carried out “signature strikes”. The US intelligence services identify a pattern that signals terrorist activities, for example a convoy of cars or a training camp. If a reconnaissance drone records signs meeting these parameters, it can attack. Sometimes the consequences have been dreadful.
Michael Hayden, retired United States Air Force general and Director of the National Security Agency in the dramatic weeks after 9/11, has said, referring to attacks against the Islamic State in Iraq, that, “The reliance on air power has all the attraction of casual sex. It seems to offer gratification but with very little commitment.” Hayden believes that such a strategy is dubious and insufficient. Now, let’s imagine a strategy where air power is in the hands of unmanned aircraft. What sort of sex would that be? President Obama has been engaging in it for years.
Jordi Pérez Colomé is a journalist specialising in international politics and author of the blog Obamaworld. He takes part in the debate Drones. Siege at a distance, that will take place on the 2nd October, in the framework of the project Under Siege.